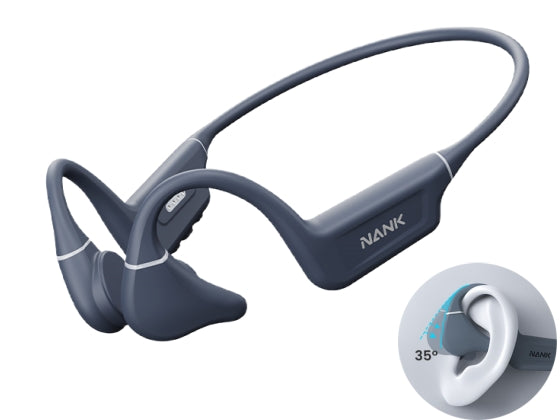
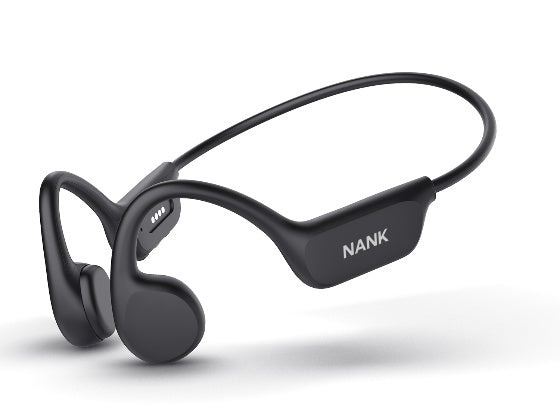
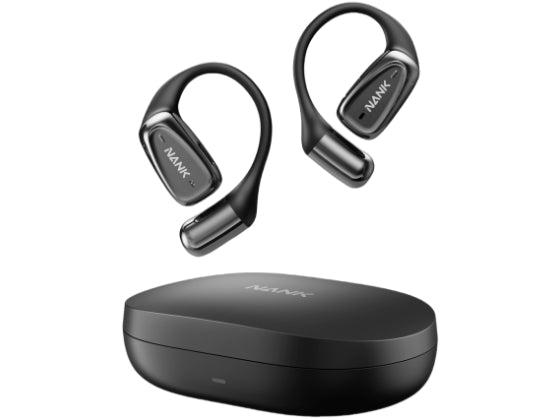
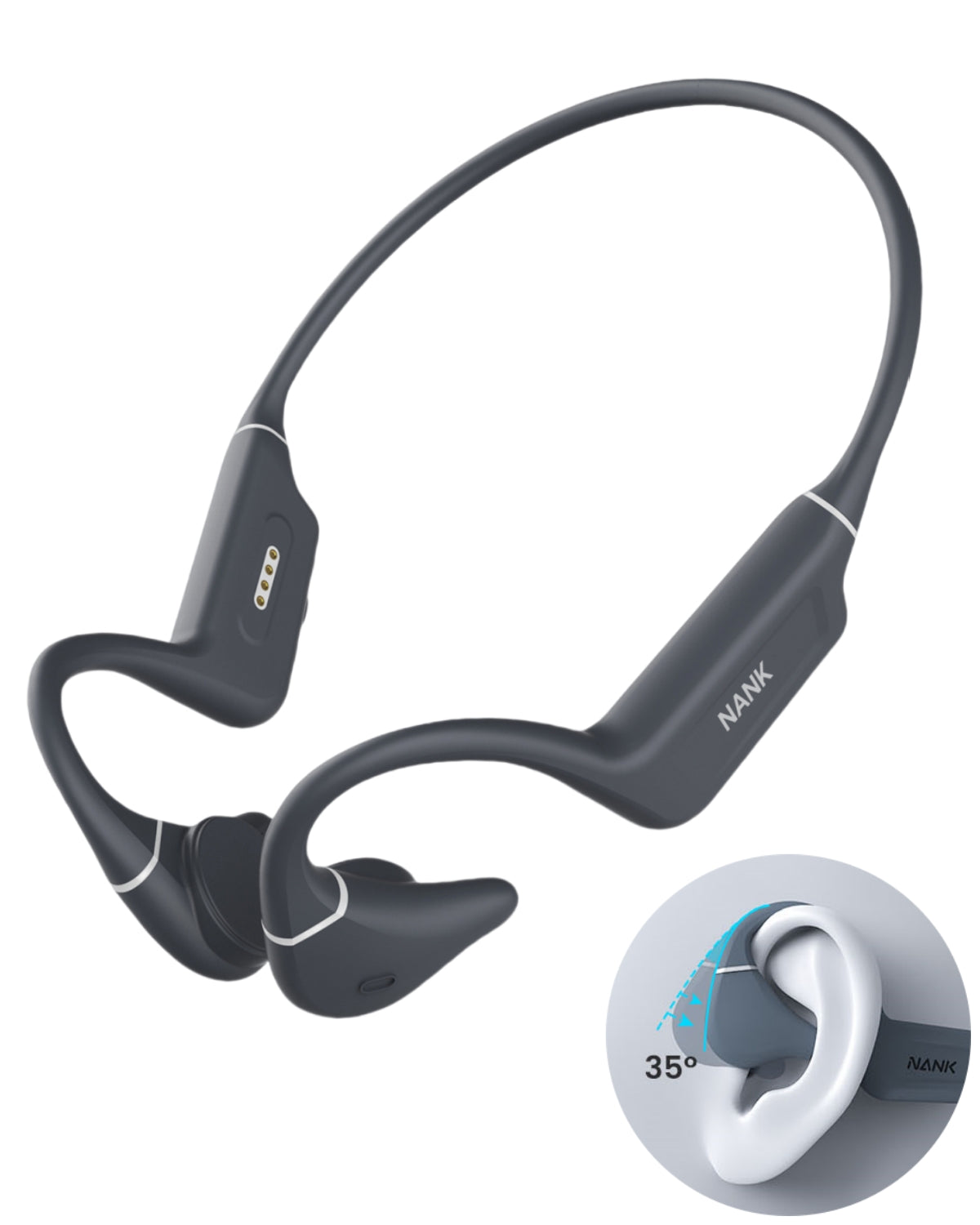
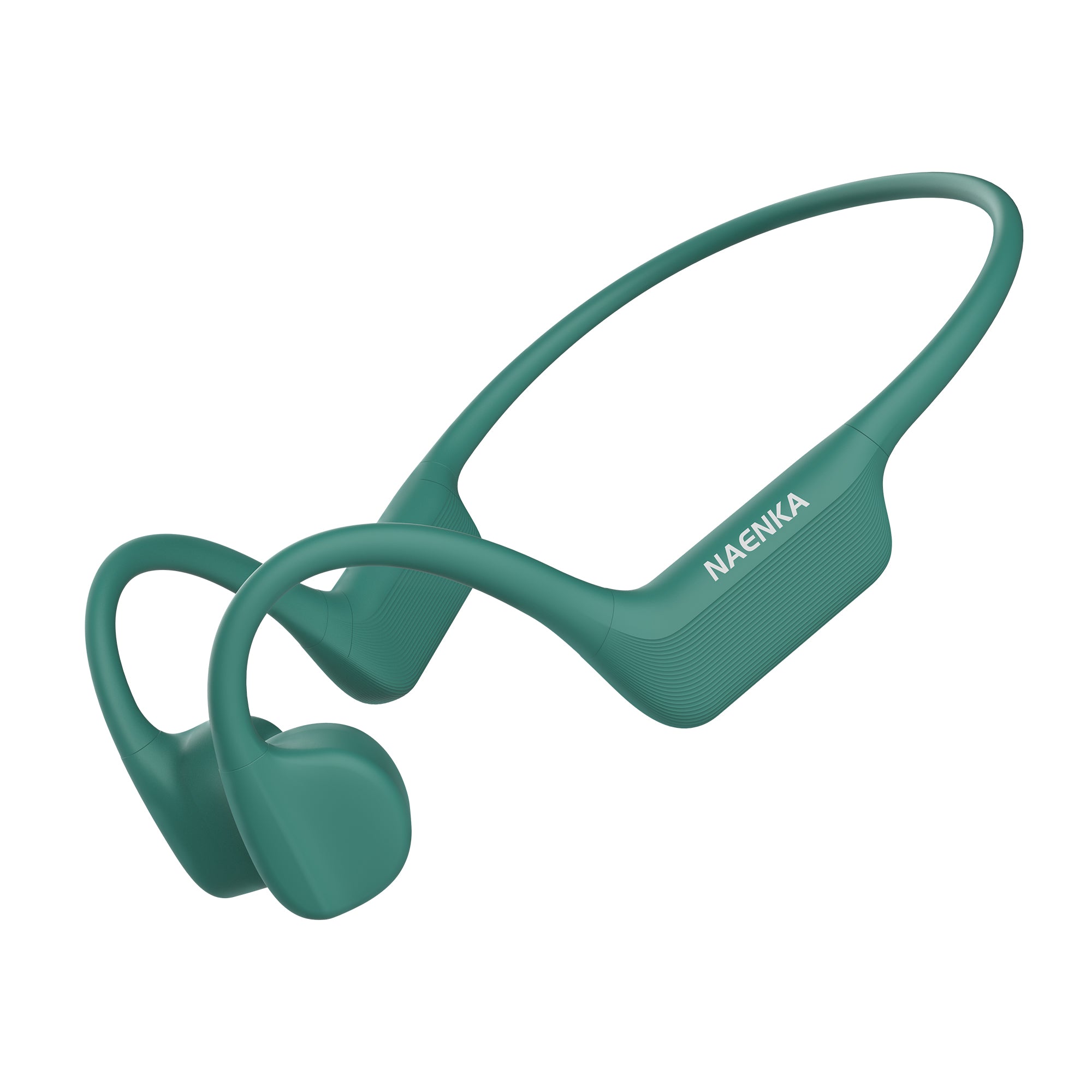
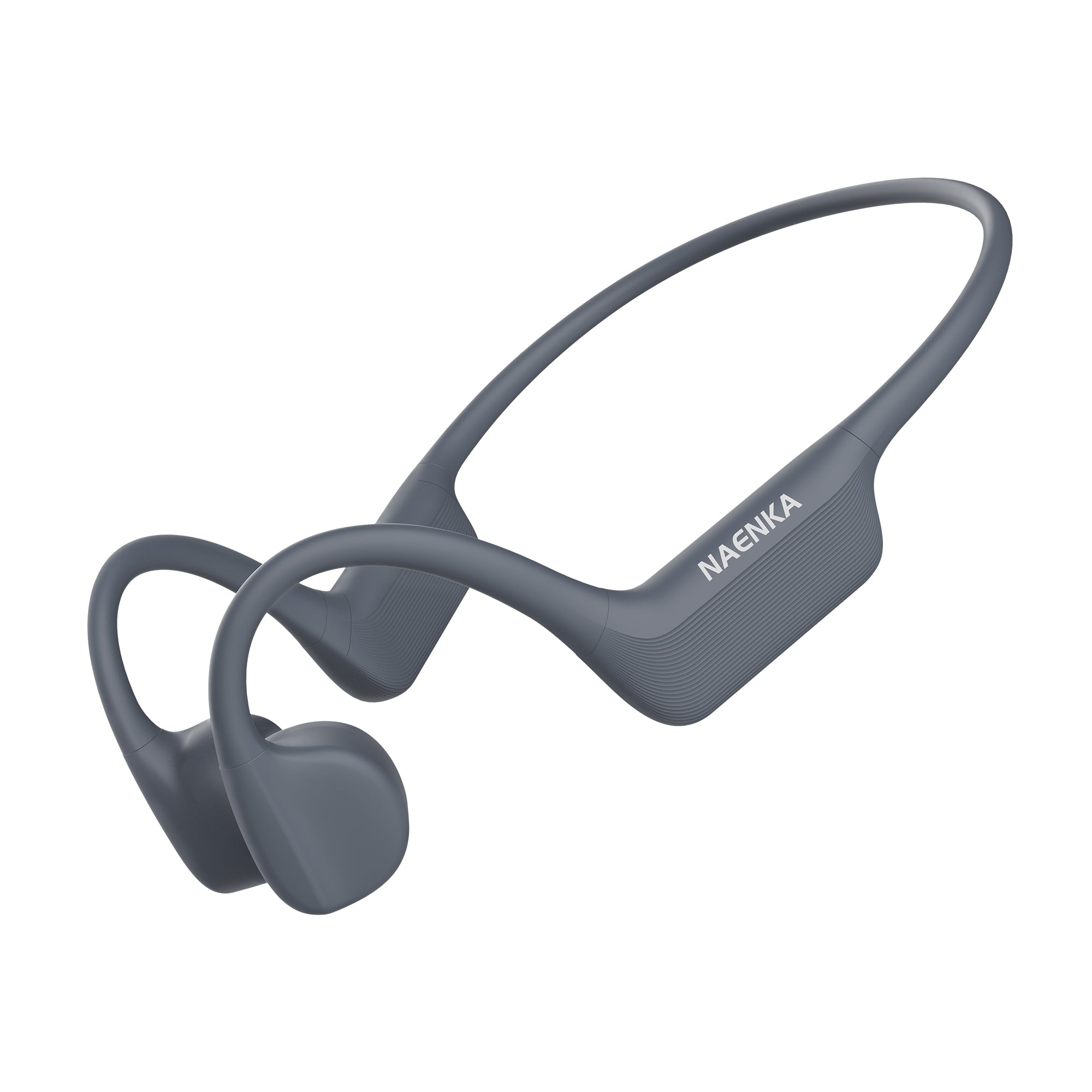
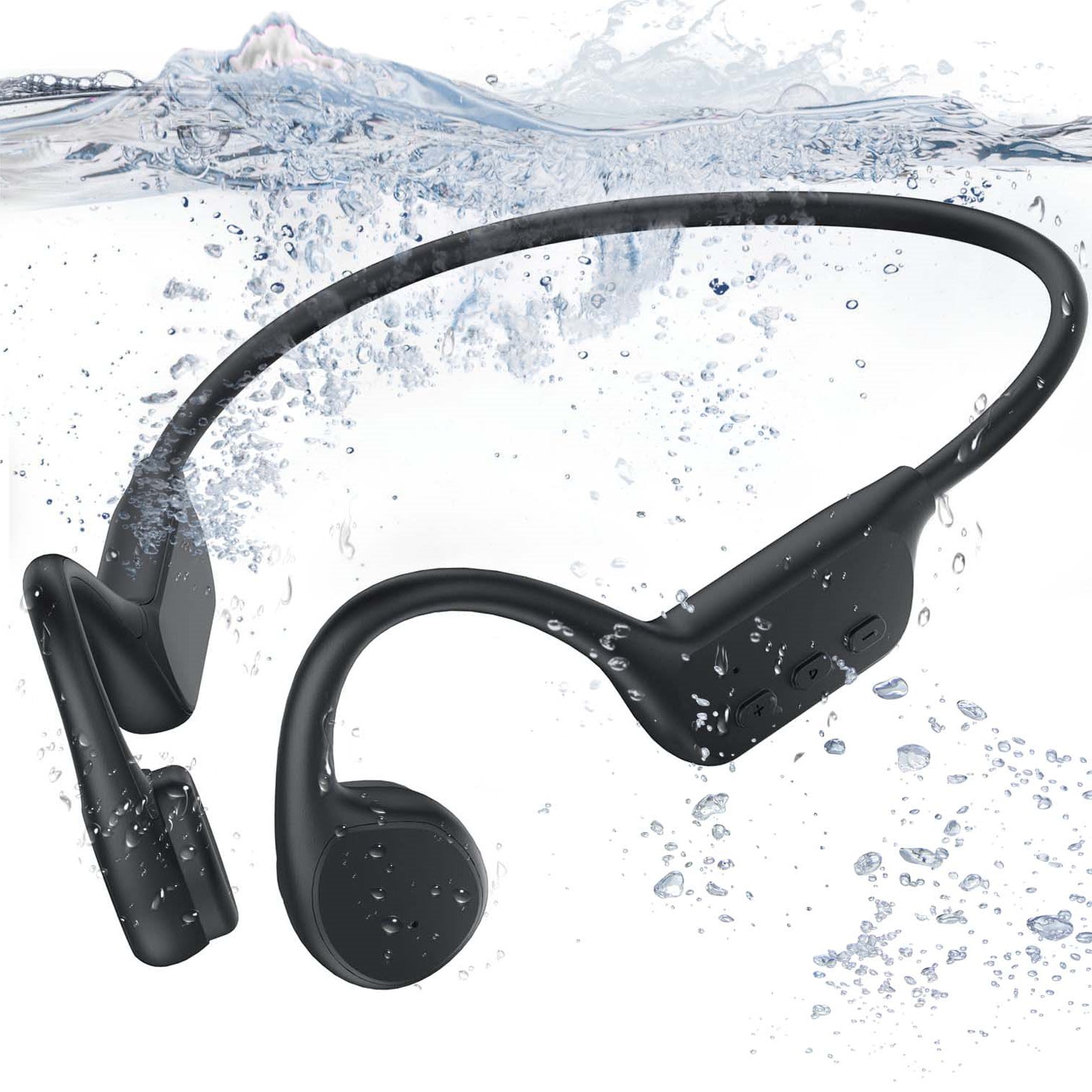
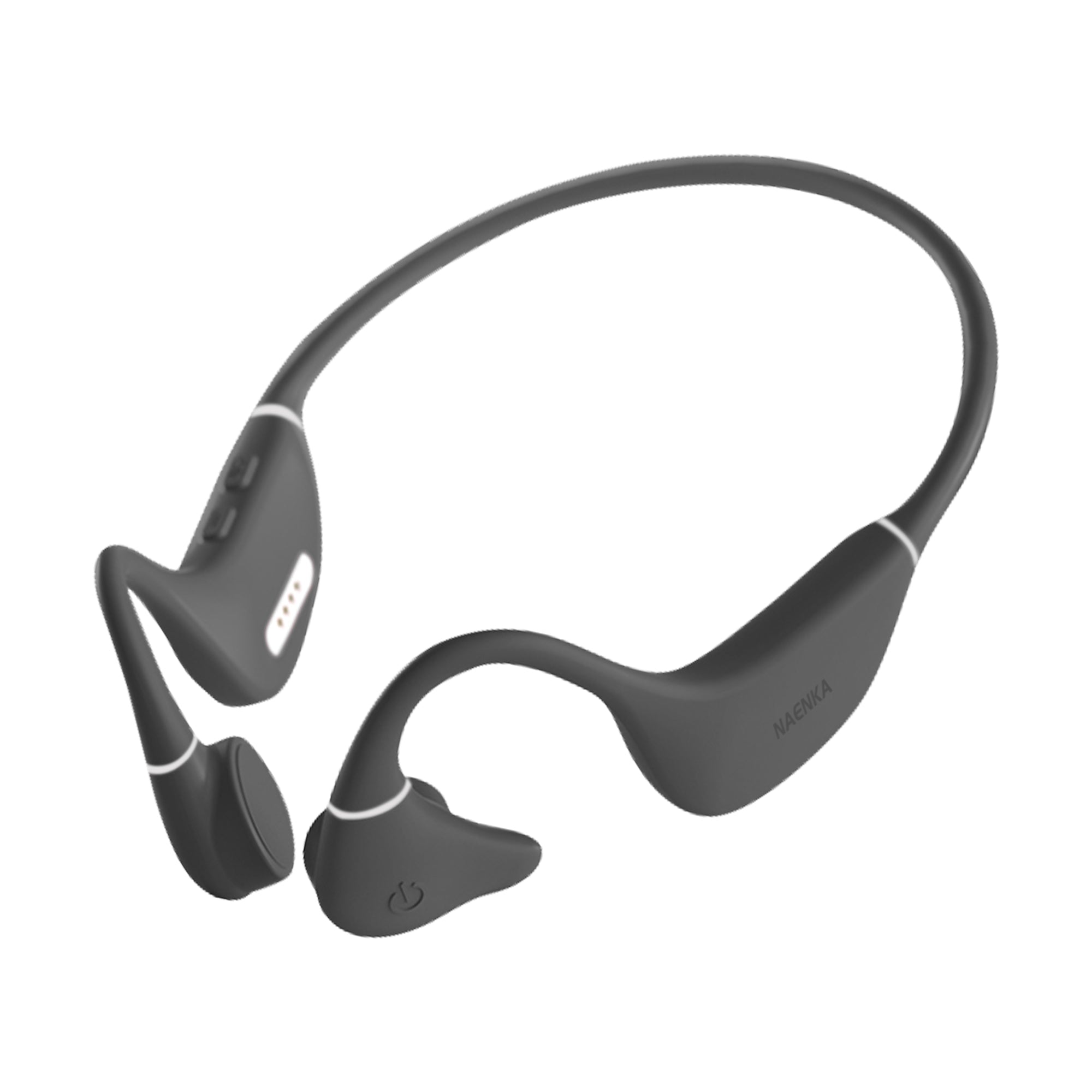
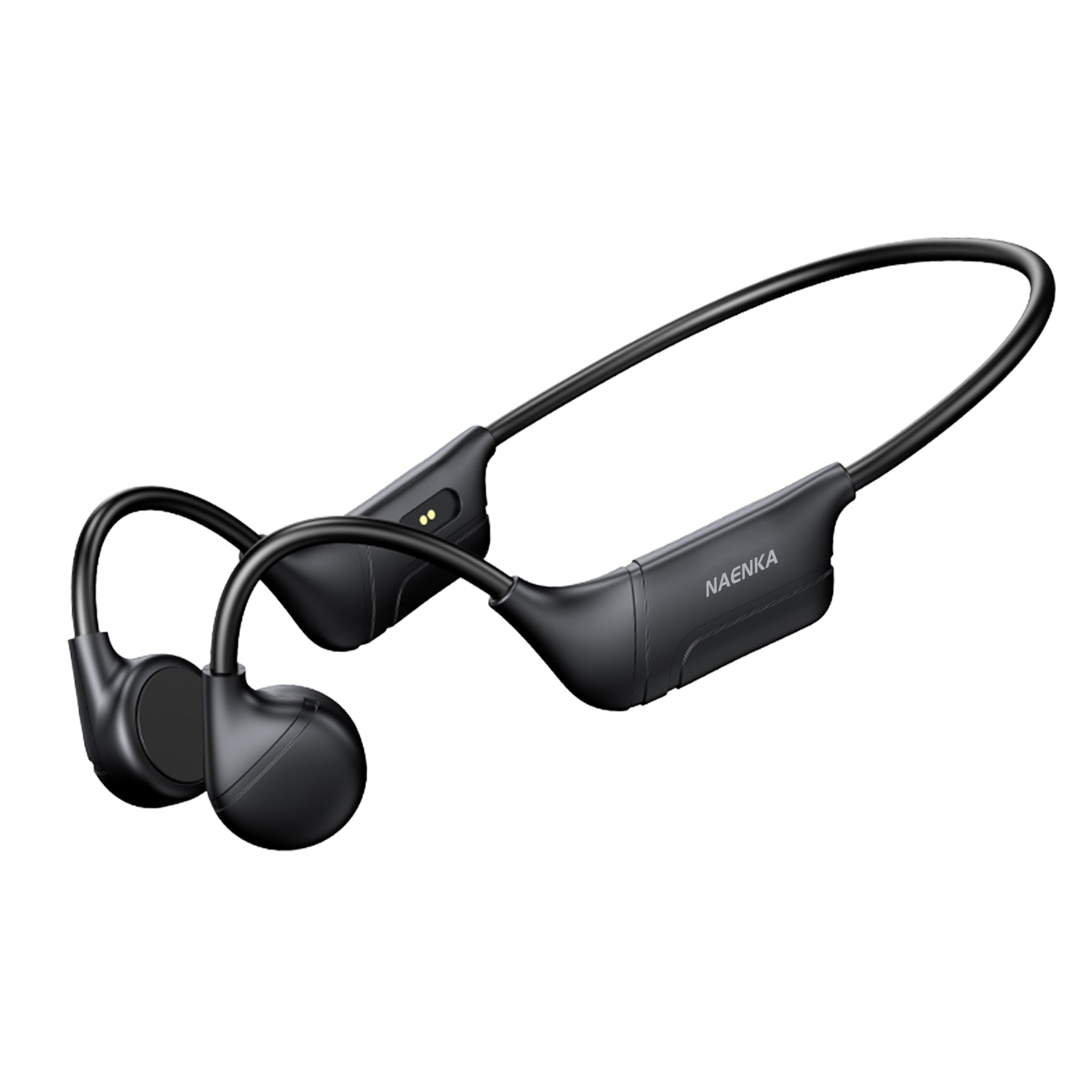
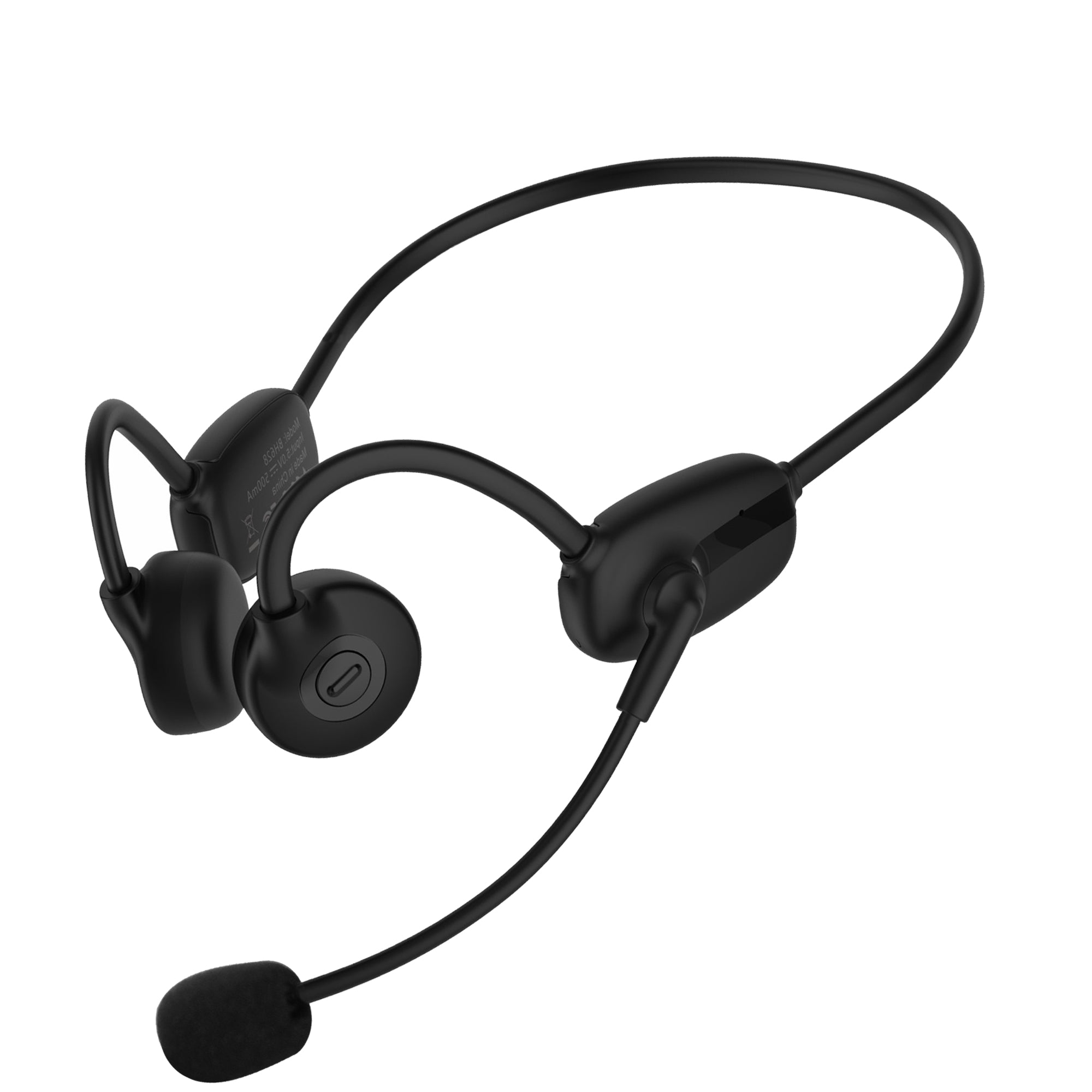
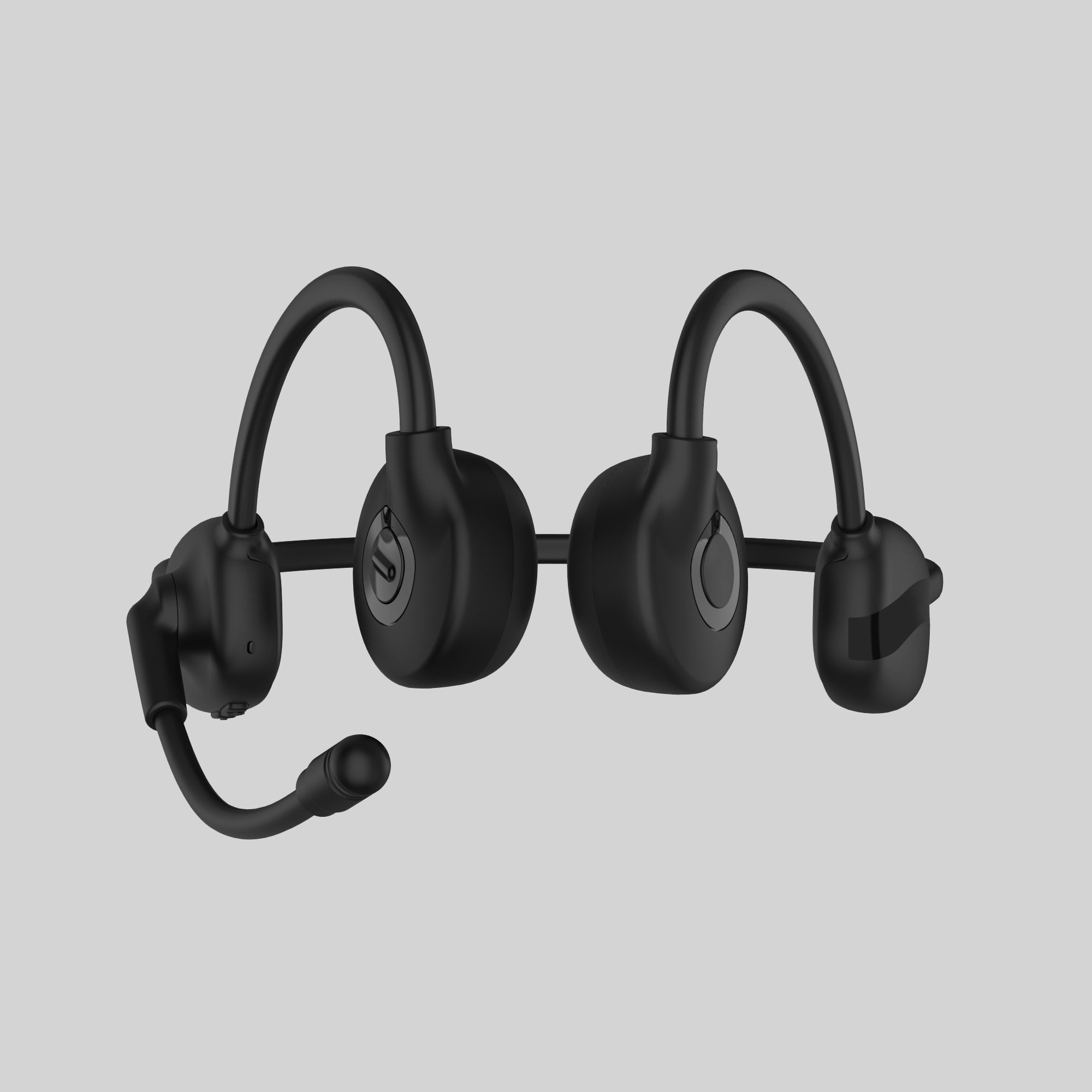
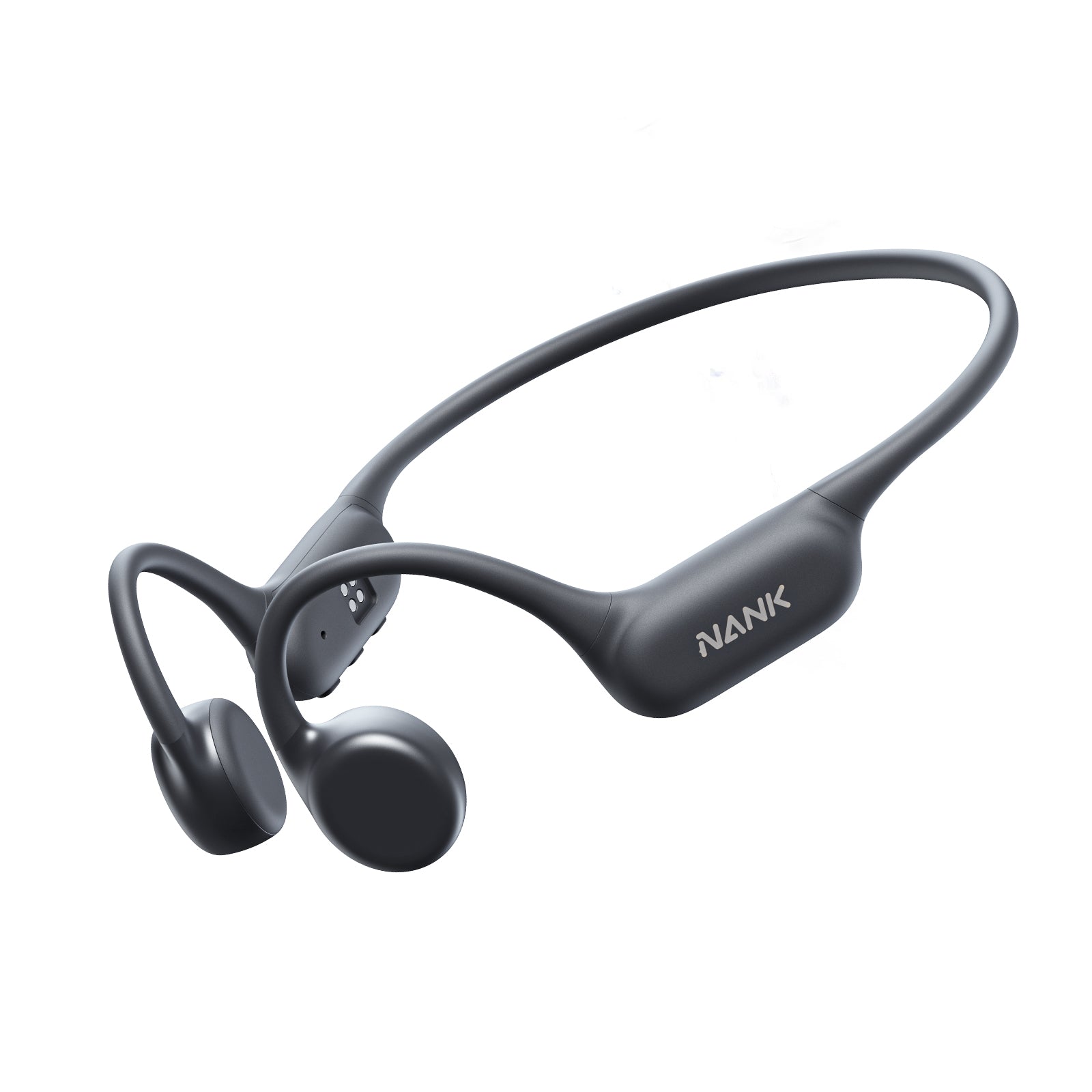
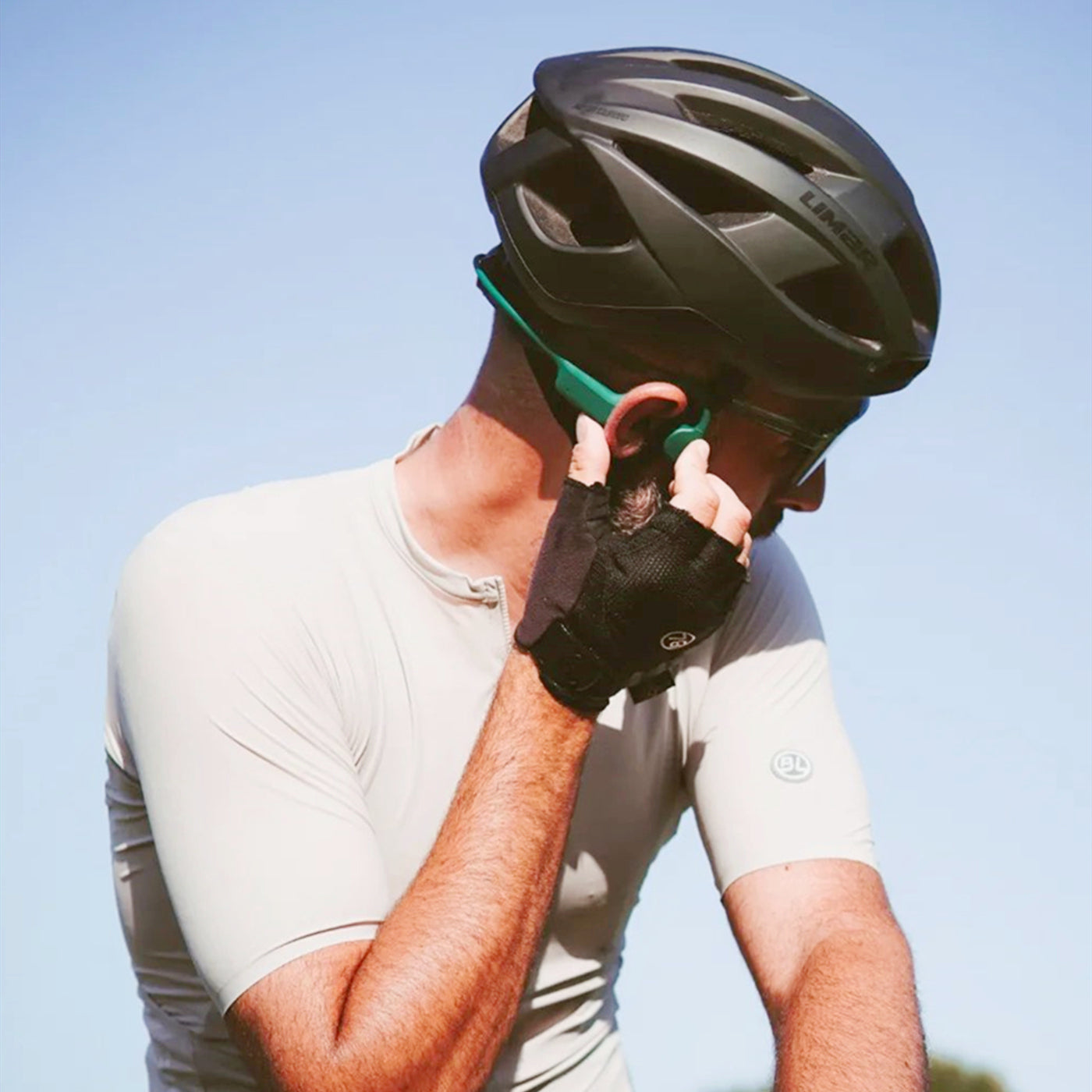
Bone conduction headphones are an emerging type of audio device. Structurally, It is composed of two vibration transducers and a housing, typically interconnected by a titanium alloy.
In comparison to traditional headphones, their primary distinction lies in the different method of sound transmission.
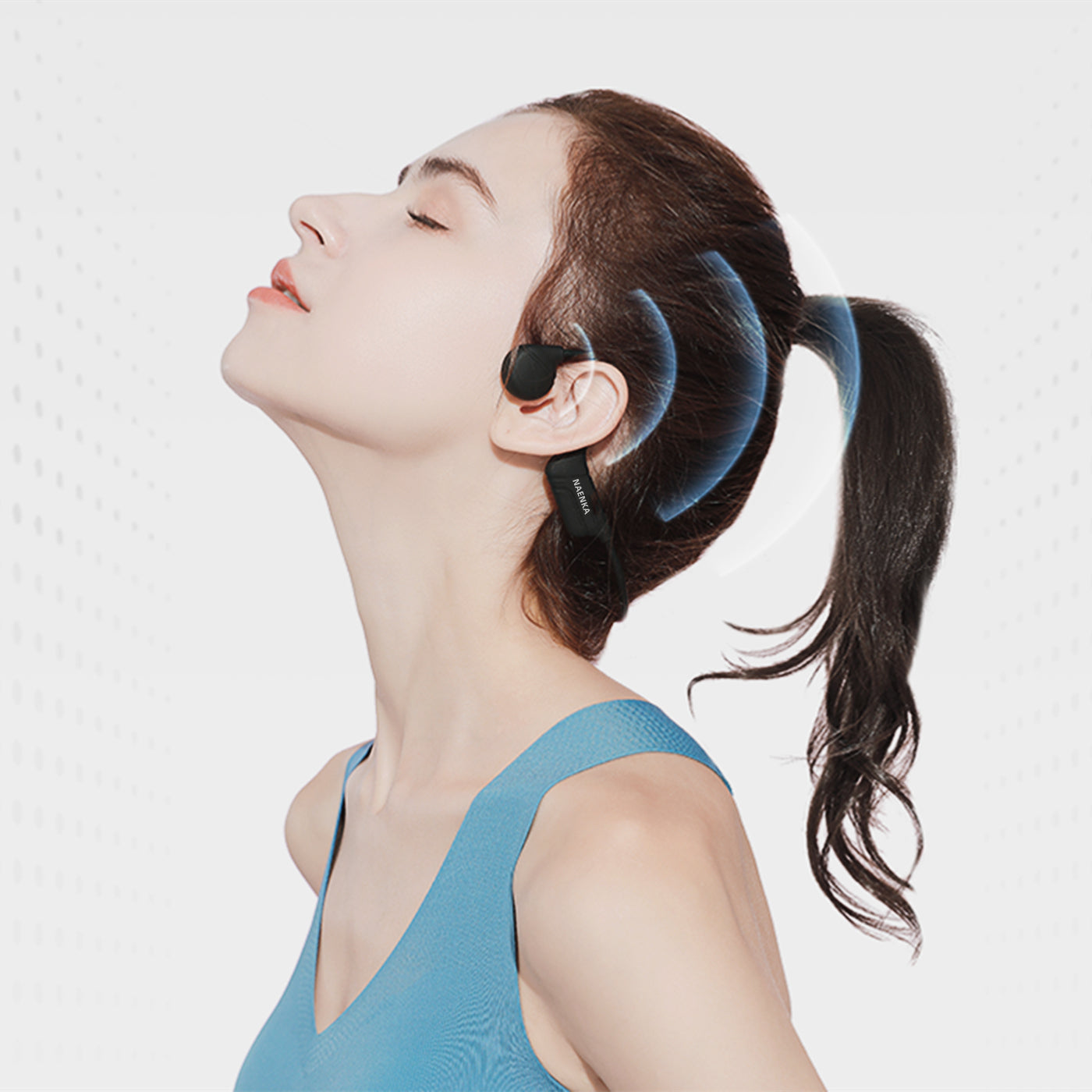
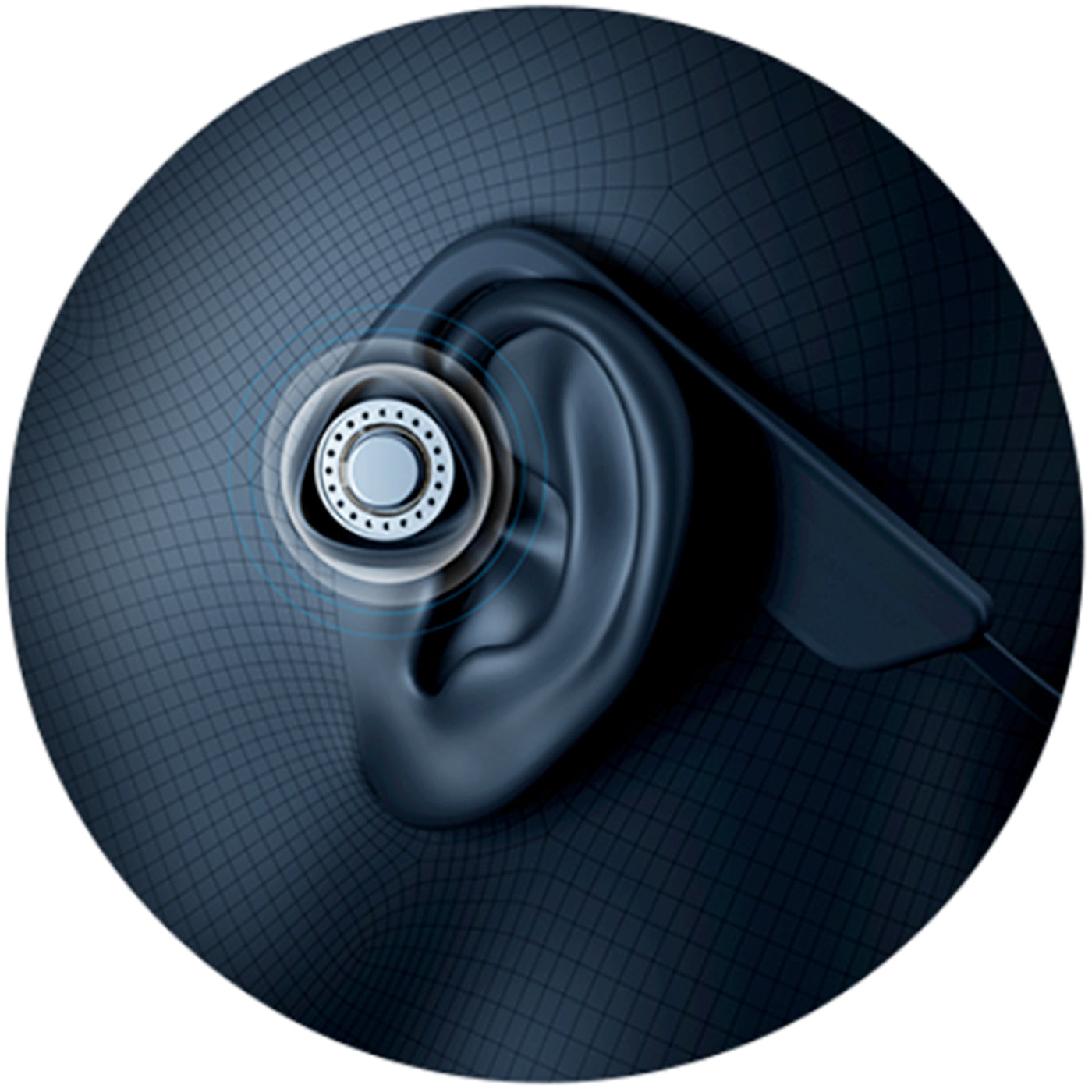
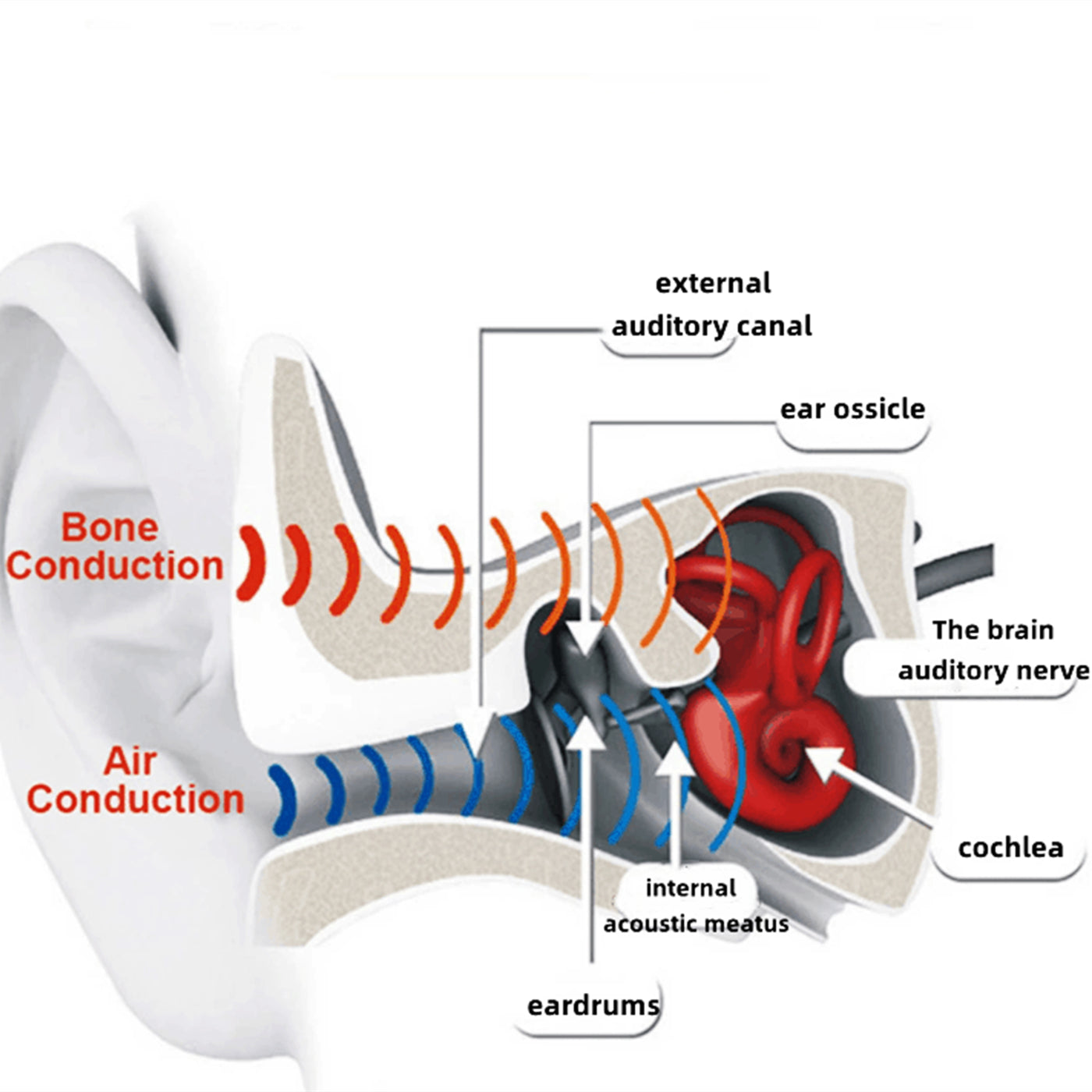
The working principle of bone conduction headphones involves the direct transmission of auditory vibrations through the skull. In contrast to conventional headphones, which rely on air-borne sound waves, bone conduction headphones convert audio signals into vibrations that travel through the skull and are perceived as sound by the inner ear. This approach eliminates the need for sound waves to pass through the ear canal.